Common Risk Factors in Cryptocurrency
- Yukun Liu, Aleh Tsyvinski and Xi Wu
- Economic Modelling, 2020
- A version of this paper can be found here
- Want to read our summaries of academic finance papers? Check out our Academic Research Insight category
What are the Research Questions?
Cryptocurrency investing is a widely debated topic and one can find plenty of debates on Twitter discussing the fed, fiat currencies, and inflation. Regardless of where you fall on the crypto spectrum, we try and focus on research-centric takes on various investment themes whenever possible.
The authors of this study research the cross-section of cryptocurrency returns and ask the following:
- Are there common risk factors that explain crypto returns?
What are the Academic Insights?
By studying all of the coins (data comes from Coinmarketcap.com) with market capitalizations above one million dollars and their returns from the beginning of 2014 ( there were a total of 109) to the end of 2018 (the total grew to 1,583) and 25 potential common factors, the authors find:
- YES, many of the known characteristics in the equity market also form successful long-short trading strategies in the cross-section of cryptocurrencies. In particular, three factors – cryptocurrency market, size, and momentum – capture most of the cross-sectional expected returns.
The authors perform a number of robustness tests to confirm the result.
Why does it matter?
This paper establishes a set of stylized facts on the cross-section of cryptocurrencies that can be used to assess and develop theoretical models.
The Most Important Chart from the Paper:
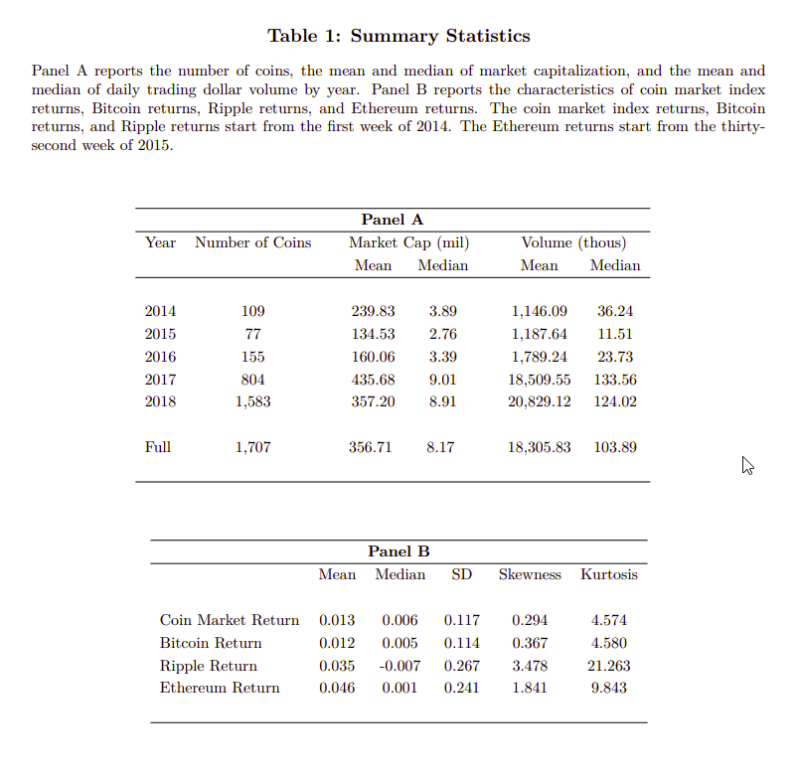
Abstract
We find that three factors—cryptocurrency market, size, and momentum—capture the cross-sectional expected cryptocurrency returns. We consider a comprehensive list of price- and market-related return predictors in the stock market and construct their cryptocurrency counterparts. Ten cryptocurrency characteristics form successful long-short strategies that generate sizable and statistically significant excess returns, and we show that all of these strategies are accounted for by the cryptocurrency three-factor model. Lastly, we examine potential underlying mechanisms of the cryptocurrency size and momentum effects.
About the Author: Elisabetta Basilico, PhD, CFA
—
Important Disclosures
For informational and educational purposes only and should not be construed as specific investment, accounting, legal, or tax advice. Certain information is deemed to be reliable, but its accuracy and completeness cannot be guaranteed. Third party information may become outdated or otherwise superseded without notice. Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) nor any other federal or state agency has approved, determined the accuracy, or confirmed the adequacy of this article.
The views and opinions expressed herein are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of Alpha Architect, its affiliates or its employees. Our full disclosures are available here. Definitions of common statistics used in our analysis are available here (towards the bottom).
Join thousands of other readers and subscribe to our blog.
