Similar to some better-known factors like size and value, time-series momentum is a factor which has historically demonstrated above-average excess returns. Time-series momentum, also called trend momentum or trend-following, is measured by a portfolio which is long assets which have had recent positive returns and short assets which have had recent negative returns.(1) Compare this to the traditional (cross-sectional) momentum factor, which considers recent asset performance only relative to other assets. The academic evidence suggests that inclusion of a strategy targeting time-series momentum in a portfolio improves the portfolio’s risk-adjusted returns. Strategies that attempt to capture the return premium offered by time-series momentum are often called, “managed futures,” as they take long and short positions in assets via futures markets — ideally in a multitude of futures markets around the globe. This piece dives into time-series momentum and examines some of its specific qualities — qualities that make a managed futures strategy a good portfolio diversifier (example shown here).
In general, an asset that has low (or negative) correlation with broad stocks and bonds provides good diversification benefits. Low or near-zero correlation between two assets means that there is no relationship in their performance: Asset A performing above average does not tell us anything about Asset B’s expected performance relative to its average. The addition of a low-correlation asset to a portfolio will, depending on the specific return and volatility properties of the asset, improve the portfolio’s risk-adjusted returns either by improving the portfolio’s return, reducing the portfolio’s volatility, or both.
An Introduction to Time Series Momentum Research
AQR Capital Management’s Brian Hurst, Yao Hua Ooi, and Lasse H. Pedersen contribute to the literature on time-series momentum with their June 2017 study, A Century of Evidence on Trend-Following Investing” — an update of their 2014 study, “Time Series Momentum.” They constructed an equal-weighted combination of one-month, three-month and 12-month time-series momentum strategies for 67 markets across four major asset classes (29 commodities, 11 equity indices, 15 bond markets and 12 currency pairs) from January 1880 to December 2016. For each of the three strategies (one-, three- and 12-month), the position taken in each market is determined by assessing the past return in that market over the relevant look-back horizon. A positive past excess return is considered an “up” trend and leads to a long position; a negative past excess return is considered a “down” trend and leads to a short position.
Each position is sized to target the same amount of volatility, both to provide diversification and to limit the portfolio risk from any one market (see risk parity for dummies). The positions across the three strategies are aggregated each month and scaled such that the combined portfolio has an annualized ex-ante volatility target of 10 percent. Volatility scaling ensures that the combined strategy targets a consistent amount of risk over time, regardless of the number of markets that are traded at each point in time. Their results include implementation costs based on estimates of trading costs in the four asset classes. They further assumed management fees of 2 percent of asset value and 20 percent of profits, a traditional fee for hedge funds.
Below is a recap of the authors’ Time Series managed futures strategy versus a long-only strategy trading the same futures contracts.
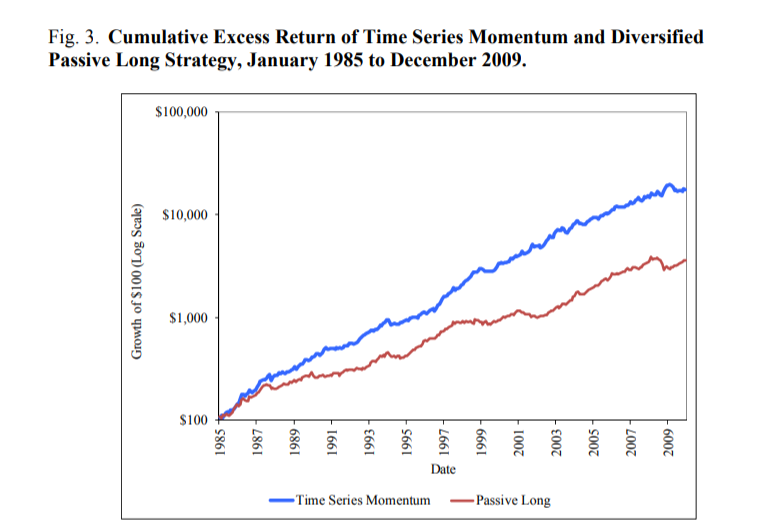
The results are hypothetical results and are NOT an indicator of future results and do NOT represent returns that any investor actually attained. Indexes are unmanaged, do not reflect management or trading fees, and one cannot invest directly in an index. Additional information regarding the construction of these results is available upon request.
The following is a summary of the AQR researchers’ findings:
- While trend-following has done particularly well in extreme up or down years for the stock market, the performance was remarkably consistent over an extensive time horizon that included the Great Depression, multiple recessions and expansions, multiple wars, stagflation, the global financial crisis of 2008, and periods of rising and falling interest rates.
- In each decade since 1880, time-series momentum has delivered positive average returns with low correlations to traditional asset classes. Further, time-series momentum has performed well in eight out of 10 of the largest crisis periods over the century, defined as the largest drawdowns for a 60/40 stock/bond portfolio — tending to perform well when its benefits were needed most.
- The persistence, pervasiveness (there were positive average returns in each of the 67 markets, with an average Sharpe ratio of approximately 0.4) and robustness (three strategies) of the results make it highly unlikely that existence of price trends in markets is a product of statistical randomness or data mining.
- Annualized returns in excess of the risk-free rate, gross of fees but net of costs, were 11.0 percent over the full period, higher than the return for equities but with about half the volatility (an annual standard deviation of 9.3 percent). After applying a 2/20 fee typical of hedge funds, the net excess return was still 7.3 percent (note that investors now have access to lower-cost alternatives in the form of publicly available mutual funds and ETFs, which also provide daily liquidity).
- Net returns were positive in every decade, with the lowest net return being the 1.6 percent return for the period beginning in 1910.
- There was virtually no correlation between either stocks or bonds. Thus, the strategy provides strong diversification benefits while producing a high Sharpe ratio (net of fees and costs) of 0.76. (Even if future returns are not as strong, the diversification benefits would justify an allocation to the strategy.) The so-called “Trend Smile,” or the historical finding that time-series momentum-based managed futures programs tend to rise in both extreme positive — and negative — markets, is compelling for investors looking to hedge their tail risks.
The chart below is from the paper:
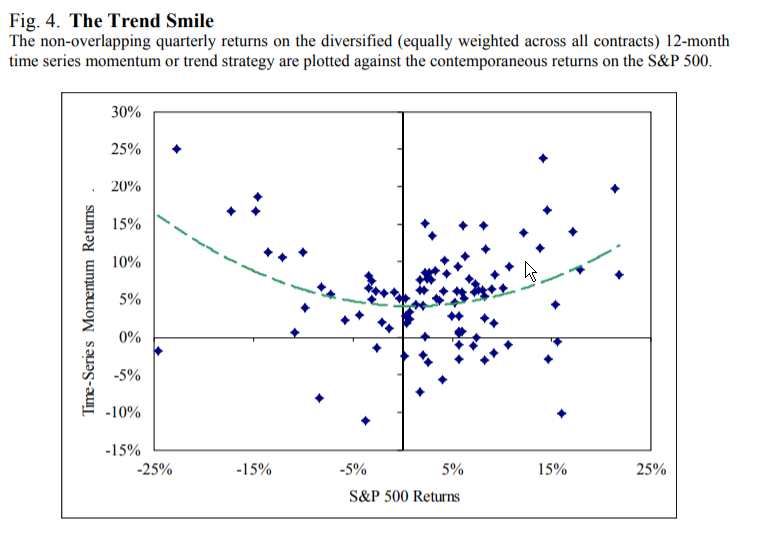
The results are hypothetical results and are NOT an indicator of future results and do NOT represent returns that any investor actually attained. Indexes are unmanaged, do not reflect management or trading fees, and one cannot invest directly in an index. Additional information regarding the construction of these results is available upon request.
- Time-series momentum is not without risk, with the strategy experiencing significant drawdowns, losing up to 25 percent over extended time periods.
The researchers at AQR observed the following:
…a large body of research has shown that price trends exist in part due to long-standing behavioral biases exhibited by investors, such as anchoring and herding [and I would add to that list the disposition effect and confirmation bias], as well as the trading activity of non-profit-seeking participants, such as central banks and corporate hedging programs. For instance, when central banks intervene to reduce currency and interest-rate volatility, they slow down the rate at which information is incorporated into prices, thus creating trends.
AQR’s researchers continued:
The fact that trend-following strategies have performed well historically indicates that these behavioral biases and non-profit-seeking market participants have likely existed for a long time.
Why is this the case? They explain:
The intuition is that most bear markets have historically occurred gradually over several months, rather than abruptly over a few days, which allows trend followers an opportunity to position themselves short after the initial market decline and profit from continued market declines…. In fact, the average peak-to-trough drawdown length of the 10 largest drawdowns of a 60 percent stocks/40 bonds portfolio between 1880 and 2016 was approximately 15 months.
AQR also noted that these results were achieved even with a “2-and-20” fee structure. Today, there are funds that can be accessed with much lower, although still not exactly cheap, expenses (including AQR’s own Managed Futures Strategy I Fund, AQMIX, which has an expense ratio of 1.22 percent, as well as the R6 version of the fund, AQMRX, which has a lower expense ratio of 1.15 percent). (Full disclosure: My firm, Buckingham Strategic Wealth, recommends AQR funds in constructing client portfolios.) Additionally, AQR has found that its actual trading costs have been much lower than the estimates used in the literature and in their own study.(2)
Time Series Momentum / Trend-Following is Pervasive
The above findings are consistent with those from prior research, such as the 2013 study by Akindynos-Nikolaos Baltas and Robert Kosowski, “Momentum Strategies in Futures Markets and Trend-Following Funds.” They studied, “The relationship between time-series momentum strategies in futures markets and commodity trading advisors (CTAs), a subgroup of the hedge fund universe that was one of the few profitable hedge fund styles during the financial crisis of 2008, hence attracting much attention and inflows in its aftermath.” The authors noted that following inflows over the subsequent years, the size of the industry had grown substantially, and CTA funds exceeded $300 billion of the total $2 trillion assets under management (AUM) invested in hedge funds by the end of 2011. Their study covered the period from December 1974 through January 2012 and included 71 futures contracts across several assets classes, specifically 26 commodities, 23 equity indices, 7 currencies, and 15 intermediate-term and long-term bonds.
The following is a summary of their findings:
- Time-series momentum exhibits strong effects across monthly, weekly and daily frequencies. See figure below from the paper:

The results are hypothetical results and are NOT an indicator of future results and do NOT represent returns that any investor actually attained. Indexes are unmanaged, do not reflect management or trading fees, and one cannot invest directly in an index. Additional information regarding the construction of these results is available upon request.
- Strategies with different rebalancing frequencies have low cross-correlations and therefore capture distinct return patterns.
- Momentum patterns are pervasive and fairly robust over the entire evaluation period and within sub-periods.
- Different strategies achieve annualized Sharpe ratios of above 1.20 and perform well in up and down markets, which render them good diversifiers in equity bear markets.
- Commodity futures-based momentum strategies have low correlation with other futures strategies. Thus, despite the fact that they have a relatively low return, they do provide additional diversification benefits.
Importantly, the authors found that momentum profitability is not limited to illiquid contracts. Rather, momentum strategies are typically implemented by means of exchange-traded futures contracts and forward contracts, which are considered relatively liquid and have relatively low transaction costs compared to cash equity or bond markets. In fact, they found the following:
for most of the assets, the demanded number of contracts for the construction of the strategy does not exceed the contemporaneous open interest reported by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) over the period 1986 to 2011.
They also found that the, “notional amount invested in futures contracts in this hypothetical scenario is a small fraction of the global OTC derivatives markets (2.3% for commodities, 0.2% for currencies, 2.9% for equities and 0.9% for interest rates at end of 2011).” Thus, they concluded:
Our analyses based on the performance-flow regressions and the hypothetical open interest exceedance scenario do not find statistically or economically significant evidence of capacity constraints in time-series momentum strategies.
Maybe Trend-Following Has Been Overdone?
Following strong performance in 2008, the aggregate performance of trend-following CTA funds has been relatively weak. For example, from January 2009 to June 2013, the annualized return of the SG CTA Trend Sub-Index (formerly the Newedge Trend Index) was -0.8 percent, versus 8.0 percent over the prior five-year period. This occurred during a period of slow recovery in the United States and prolonged crisis in the Eurozone. Relatively poor performance, combined with large inflows following the strong performance, leads investors to question both whether the trend-following strategy has already become too crowded and if it will work in the future.
See below for the chart from the paper which highlights the AUM surge in CTA funds:
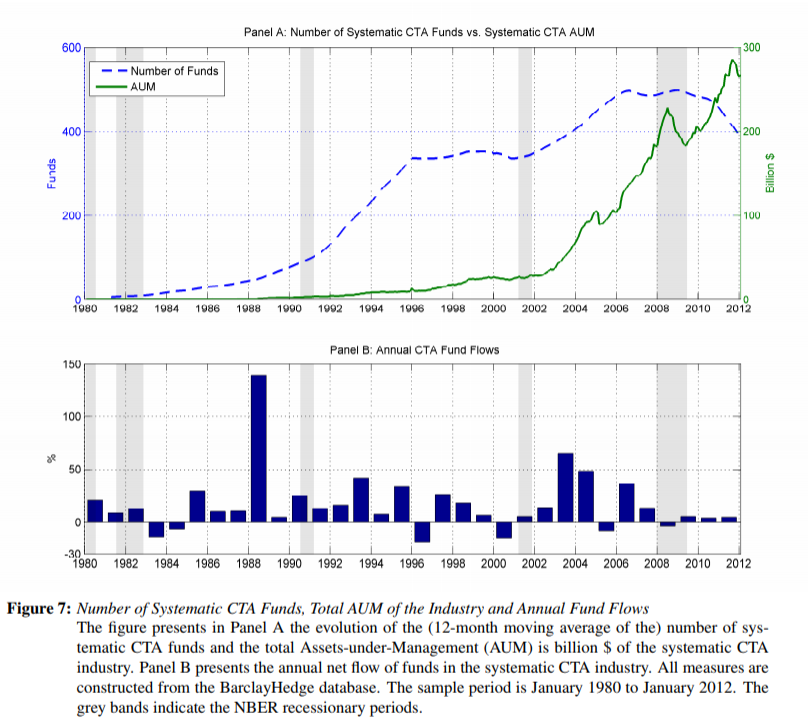
The results are hypothetical results and are NOT an indicator of future results and do NOT represent returns that any investor actually attained. Indexes are unmanaged, do not reflect management or trading fees, and one cannot invest directly in an index. Additional information regarding the construction of these results is available upon request.
Support for time-series momentum also comes from the 2014 study, “Is This Time Different? Trend Following and Financial Crises.” Using almost a century of data on trend-following, the authors, Mark C. Hutchinson and John O’Brien, investigated what happened to the performance of the strategy subsequent to the U.S. subprime and Eurozone crises and whether it was typical of what happens after a financial crisis. They note: “Identifying a list of global and regional financial crises is problematic.” Thus, they chose to use the list of crises from two of the most highly cited studies on financial crises, “Manias, Panics, and Crashes: A History of Financial Crises” (originally published in 1978) and “This Time Is Different: Eight Centuries of Financial Folly” (originally published in 2009). The six global crises studied were:
- The Great Depression in 1929
- The 1973 Oil Crisis
- The Third World Debt crisis of 1981
- The Crash of October 1987
- The bursting of the dot-com bubble in 2000
- Sub-Prime/Euro crisis beginning in 2007
The regional crises studied (with year of inception in parentheses) were as follows:
- Spain (1977)
- Norway (1987)
- Nordic (1989)
- Japan (1990)
- Mexico (1994)
- Asia (1997)
- Colombia (1997)
- Argentina (2000)
The start date for each crisis was the month following the equity market high preceding the crisis. Because neither of the two aforementioned studies provided guidance on the length or end date of each crisis, rather than attempting to define when each individual crisis finished, the authors instead focused on two fixed time periods: 24 months and 48 months after the prior equity market high.
Hutchinson and O’Brien’s dataset for the global analysis consisted of 21 commodities, 13 government bonds, 21 equity indices, and currency crosses derived from nine underlying exchange rates covering a sample period from January 1921 to June 2013. Their results include estimates of trading costs as well as the typical hedge fund fee of 2 percent of assets and 20 percent of profits.
The following is a summary of their findings:
- Time-series momentum has been highly successful over the long term. The average net return for the global portfolio from 1925 to 2013 was 12.1 percent, with a volatility of 11 percent. The Sharpe ratio was an impressive 1.1 (a finding consistent with that of other research).
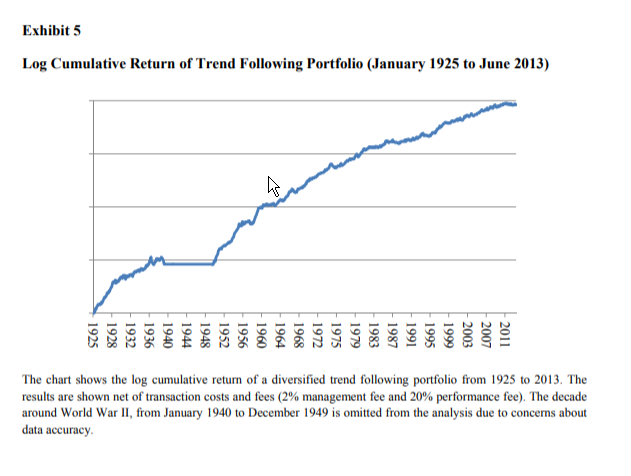
The results are hypothetical results and are NOT an indicator of future results and do NOT represent returns that any investor actually attained. Indexes are unmanaged, do not reflect management or trading fees, and one cannot invest directly in an index. Additional information regarding the construction of these results is available upon request.
- There is a breakdown in futures market return predictability during crisis periods.
- In no-crisis periods, market returns exhibit strong serial correlation at lags of up to 12 months.
- Subsequent to a global financial crisis, trend-following performance tends to be weak for four years on average. This lack of time-series return predictability reduces the opportunity for trend-following to generate returns.
- Comparing the performance of crisis and no-crisis periods, the average return (4.0 percent) in the first 24 months following the start of a crisis is less than one-third of the return (13.6 percent) earned in no-crisis periods. Performance in the 48 months after a crisis starts (6.0 percent) was well under half the return (14.9 percent) in that of no-crisis periods.
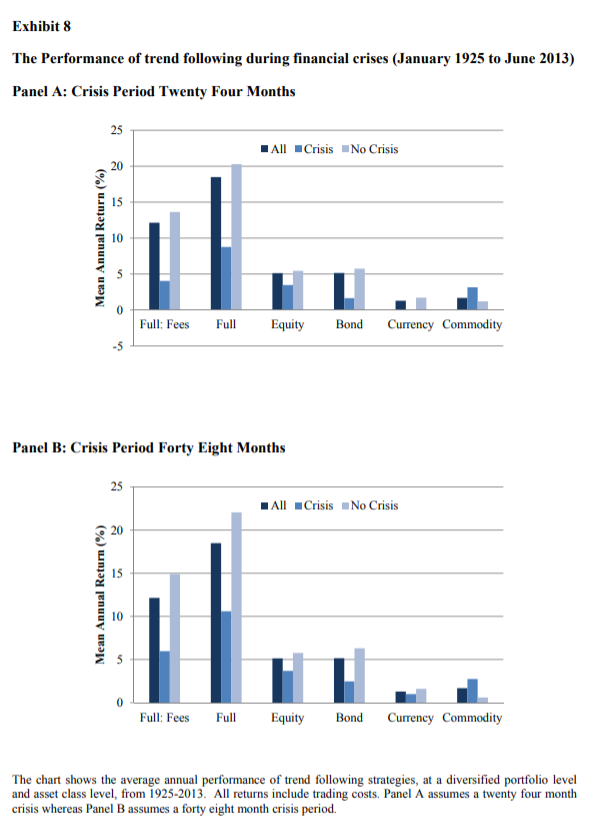
The results are hypothetical results and are NOT an indicator of future results and do NOT represent returns that any investor actually attained. Indexes are unmanaged, do not reflect management or trading fees, and one cannot invest directly in an index. Additional information regarding the construction of these results is available upon request.
- Across stocks, bonds, and currencies, the results were consistent. The exception was commodities, where returns were of similar magnitude in pre- and post-crisis periods.
- They found a similar effect when examining portfolios formed of local assets during regional financial crises.
The authors noted that behavioral models link momentum to investor overconfidence and decreasing risk aversion, with both leading to return predictability in asset prices. Under these models, overconfidence should fall and risk aversion should increase following market declines, so it seems logical that return predictability would fall following a financial crisis. It is also important to note, as the authors did, that, “governments have an increased tendency to intervene in financial markets during crises, resulting in discontinuities in price patterns.” Such interventions can lead to sharp reversals, with negative consequences for trend-following.
Hutchinson and O’Brien concluded:
The performance of these types of [trend-following] strategies is much weaker in crisis periods, where performance can be as little as one-third of that in normal market conditions. This result is supported by our evidence for regional crises, though the effect seems to be more short-lived. In our analysis of the underlying markets, our empirical evidence indicates a breakdown in the time series predictability, pervasive in normal market conditions, on which trend following relies.
Time Series and Trend-Following: Summarizing the Evidence
As an investment style, trend-following has existed for a long time. The data from the aforementioned studies provide strong out-of-sample evidence beyond the substantial evidence that already existed in the literature. It also provides consistent, long-term evidence that trends have been pervasive features of global stock, bond, commodity and currency markets.
Addressing the issue of whether we should expect trends to continue, the AQR researchers concluded:
The most likely candidates to explain why markets have tended to trend more often than not include investors’ behavioral biases, market frictions, hedging demands, and market interventions by central banks and governments. Such market interventions and hedging programs are still prevalent, and investors are likely to continue to suffer from the same behavioral biases that have influenced price behavior over the past century, setting the stage for trend-following investing going forward.
The bottom line is that, given the diversification benefits and the downside (tail-risk) hedging properties, I believe that a moderate portfolio allocation to trend-following strategies merits consideration. Note that the generally high turnover of trend-following strategies renders them relatively tax inefficient. Thus, there should be a strong preference to hold them in tax-advantaged accounts.
References[+]
| ↑1 | See here for a full course on trend-following by Valeriy Zakamulin |
|---|---|
| ↑2 | Editor’s Note: Alpha Architect offers various managed futures strategies as well, but they are only accessible via separately managed accounts and have large minimum investments ($1mm+). |
About the Author: Larry Swedroe
—
Important Disclosures
For informational and educational purposes only and should not be construed as specific investment, accounting, legal, or tax advice. Certain information is deemed to be reliable, but its accuracy and completeness cannot be guaranteed. Third party information may become outdated or otherwise superseded without notice. Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) nor any other federal or state agency has approved, determined the accuracy, or confirmed the adequacy of this article.
The views and opinions expressed herein are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of Alpha Architect, its affiliates or its employees. Our full disclosures are available here. Definitions of common statistics used in our analysis are available here (towards the bottom).
Join thousands of other readers and subscribe to our blog.

