This paper investigates the significant role of transaction costs in FX markets, particularly focusing on the impact of trading volume on these costs and their effects on the profitability of various currency trading strategies.
Importance of transaction costs for asset allocation in foreign exchange markets
- Ilias Filippou Thomas A. Maurer Luca Pezzo and Mark P. Taylor
- Journal of Financial Economics, 2024
- A version of this paper can be found here
- Want to read our summaries of academic finance papers? Check out our Academic Research Insight category
What are the Research Questions?
The research questions are as follows:
- What is the impact of trading volume on transaction costs in FX markets?
- How sensitive are popular currency trading strategies to the price impact of trading?
- Can a mean-variance-transaction-cost optimization approach mitigate trading costs while maintaining profitability?
- What insights can be drawn about FX market illiquidity and its effects on currency trading strategies?
What are the Academic Insights?
By focusing on daily bid, ask and mid quotes for spot and forward exchange rates of 26 countries, the authors find:
- The impact of trading volume on transaction costs in FX markets is significant, particularly through the price impact of trading. High trading volumes can lead to substantial transaction costs, which have first-order negative implications on the profitability of currency trading strategies. This is because large trade orders, especially from sizable funds, can move bid and ask quotes, increasing costs due to the price impact.
- Popular currency trading strategies are highly sensitive to the price impact of trading. The study finds that strategies such as the currency carry trade, momentum, and mean-variance optimized currency portfolios see their returns significantly eroded by the costs associated with the price impact of trading.
- YES, a mean-variance-transaction-cost optimization (MVTC) approach can mitigate trading costs while maintaining profitability. The paper introduces the MVTC approach, which builds on the mean-variance optimized currency portfolio and incorporates a framework to tackle transaction costs. It can : Reduce Trading Activity in Costly Currencies; Maintain Near-Optimal Balance Between Return and Risk; Increase the Capacity of the Strategy
- Here are the key insights regarding FX market illiquidity and its effects on currency trading strategies:
- Market illiquidity significantly increases transaction costs, impacting the profitability of trading strategies.
- Strategies like currency carry trades and momentum trading are highly sensitive to changes in market liquidity.
- Effective risk management in FX trading requires strategies that can adapt to varying liquidity conditions.
- FX market illiquidity may lead to the existence of illiquidity premia, reflecting higher risks associated with trading less liquid currencies.
- Strategies capable of navigating FX market illiquidity tend to exhibit more stable long-term performance.
Why does this study matter?
It provides crucial insights into how transaction costs, particularly driven by trading volume and liquidity conditions, can significantly impact the profitability of currency trading strategies. Understanding these dynamics helps investors and portfolio managers better manage their trading activities and optimize their strategies to mitigate costs.
The Most Important Chart from the Paper:
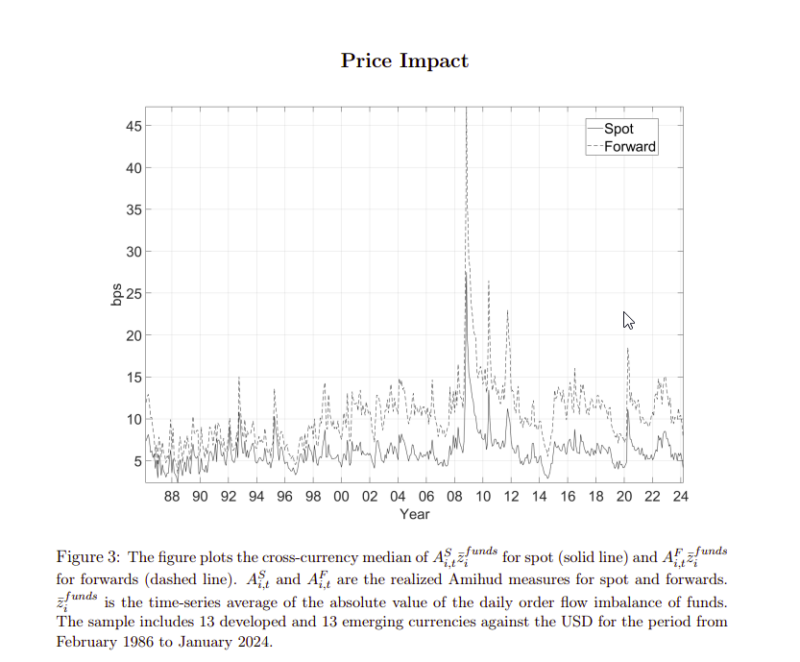
The results are hypothetical results and are NOT an indicator of future results and do NOT represent returns that any investor actually attained. Indexes are unmanaged and do not reflect management or trading fees, and one cannot invest directly in an index.
Abstract
Transaction costs have a first-order effect on the performance of currency portfolios. Proportional costs based on quoted bid–ask spread are relatively small, but when a fund is large, costs due to the trading volume price impact are sizable and quickly erode returns, leaving many popular strategies unprofitable. A mean–variance-transaction-cost optimized approach (MVTC) that accounts for costs in the optimization efficiently tackles the problem with only relatively minor negative implications on before-cost profitability. MVTC is robust even when the price impact of trading is severe. Finally, we introduce an accurate extrapolation approach to expand the sample of the realized Amihud measure of Ranaldo and Santucci de Magistris (2022) from 12 to 26 currencies and from 2012 back in time to 1986.
About the Author: Elisabetta Basilico, PhD, CFA
—
Important Disclosures
For informational and educational purposes only and should not be construed as specific investment, accounting, legal, or tax advice. Certain information is deemed to be reliable, but its accuracy and completeness cannot be guaranteed. Third party information may become outdated or otherwise superseded without notice. Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) nor any other federal or state agency has approved, determined the accuracy, or confirmed the adequacy of this article.
The views and opinions expressed herein are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of Alpha Architect, its affiliates or its employees. Our full disclosures are available here. Definitions of common statistics used in our analysis are available here (towards the bottom).
Join thousands of other readers and subscribe to our blog.

