Effects of amount of information on judgment accuracy and confidence
- Claire I. Tsai, Joshua Klayman, Reid Hastie
- A version of the paper can be found here.
- Want a summary of academic papers with alpha? Check out our free Academic Alpha Database!
Abstract:
When a person evaluates his or her confidence in a judgment, what is the effect of receiving more judgment-relevant information? We report three studies that show when judges receive more information, their confidence increases more than their accuracy, producing substantial confidence–accuracy discrepancies. Our results suggest that judges do not adjust for the cognitive limitations that reduce their ability to use additional information effectively. We place these findings in a more general framework of understanding the cues to confidence that judges use and how those cues relate to accuracy and calibration.
Data Sources:
Survey Evidence
Alpha Highlight:
Empiritrage has a detailed report here
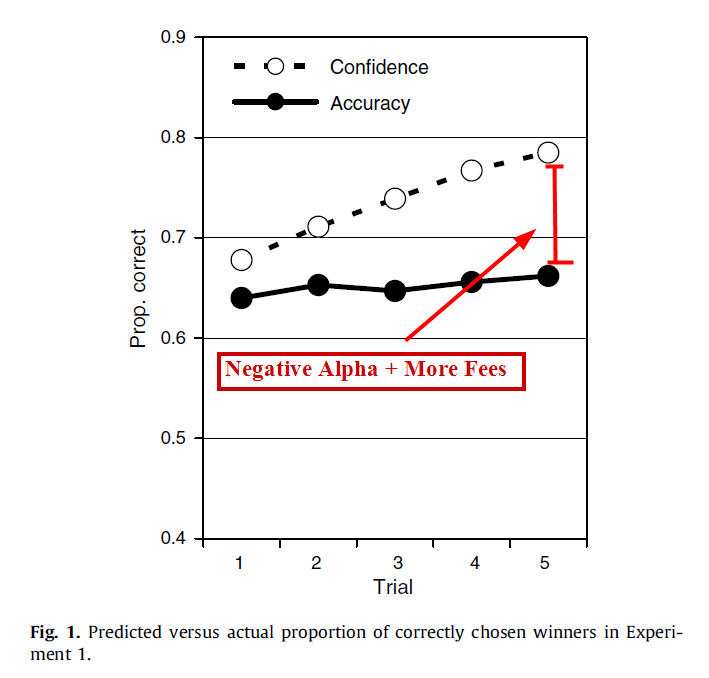
The results are hypothetical results and are NOT an indicator of future results and do NOT represent returns that any investor actually attained. Indexes are unmanaged, do not reflect management or trading fees, and one cannot invest directly in an index. Additional information regarding the construction of these results is available upon request.
About the Author: Wesley Gray, PhD
—
Important Disclosures
For informational and educational purposes only and should not be construed as specific investment, accounting, legal, or tax advice. Certain information is deemed to be reliable, but its accuracy and completeness cannot be guaranteed. Third party information may become outdated or otherwise superseded without notice. Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) nor any other federal or state agency has approved, determined the accuracy, or confirmed the adequacy of this article.
The views and opinions expressed herein are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of Alpha Architect, its affiliates or its employees. Our full disclosures are available here. Definitions of common statistics used in our analysis are available here (towards the bottom).
Join thousands of other readers and subscribe to our blog.

